The information stored in a database is organized into records and fields. Each field contains a specific category of information — names, phone numbers, birthdates, etc. Your first task after creating a new database is to decide how many and what fields are needed to get the job done. It’s somewhat like designing a house — you have to decide what the best configuration is. How many bedrooms do you need? How many baths? Will you need an office? And just like architecture, there are sometimes trade-offs that have to be made in designing a database.
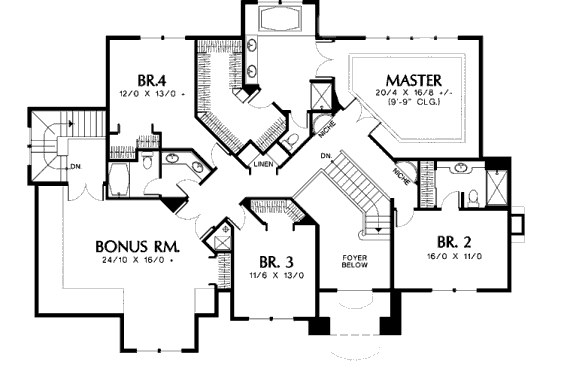
For some database jobs it is extremely obvious how the fields should be set up. But usually you have more flexibility than you might think. Take a simple name and address list, probably one of the most basic database applications. How should the name be stored? All in one field? Or should there be separate fields for first and last names? What about Mr./Ms./Mrs., should that be in a separate field? There are no hard and fast answers — it depends on how you want to use the database. For this example (names), data entry will probably be easier if you use a single field. On the other hand, you’ll have more options for organizing and formatting if you split the name into several fields. The choice is up to you.
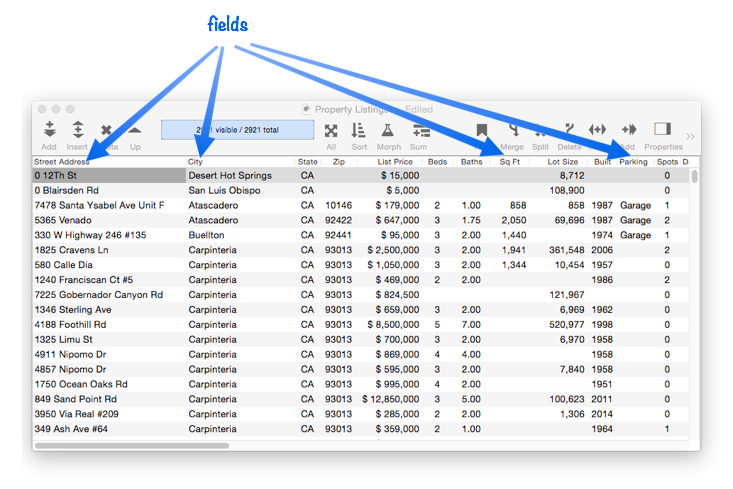
One thing to keep in mind is that if you make a mistake, it is much easier to combine two fields together than it is to split a single field into two. For example, it is quite easy to take separate first and last name fields and combine them, but if you type the names into a single field it could be quite difficult to later split them apart. If you have any doubt, it is better to err on the side of separating the data into more fields.
You can add new fields, remove fields, or change the properties of fields at any time, even after you’ve filled the database with data. Once you start entering data, however, it can be more work to re-arrange the fields. Some extra planning before you start entering data can pay big dividends in the long run.
Note: The data sheet is normally limited to 150 visible columns at a time. If you need to use more than 150 fields, see Limiting the Maximum Number of Data Sheet Columns.
See Also
- addfield -- adds a new field to the current database (on the end).
- Adding New Fields -- adding one or more fields to a database.
- autoallfieldwidths -- automatically sets the width of all fields based on the data in each field.
- autofieldwidth -- automatically sets the width of the current field based on the data in it.
- Automatic Field Calculations -- performing formulas automatically when data is entered into a field.
- Automatic Field Code -- running a short program when data is entered into a field.
- automaticfieldchoices -- updates the current field's Choice list with actual data in the database.
- automaticfieldname( -- returns an available field name.
- cell -- enters a value into the currently active field (i.e. cell).
- checkdesignlock -- checks if field structure can be changed, if not, returns an error.
- commonfieldspopup -- pops up a list of common fields, and changes the current field specifications when a field is chosen from this menu.
- Construct Multiple Fields -- using a template to quickly add multiple fields to a database.
- constructfields -- creates one or more new fields based on a template.
- databaseconsoledump -- dumps the raw contents of the specified database to the console in comma delimited format.
- Date Patterns -- control how dates are displayed or converted to text.
- Dates -- working with dates.
- dbinfo( -- gets information about a database: what forms it contains, what fields, what flash art pictures, etc.
- deletefield -- deletes the current field from the database.
- Deleting Fields -- deleting fields from the database.
- Disable Editing of Individual Fields -- disable editing of inidividual database fields in the data sheet and/or forms.
- disablefieldediting -- disables editing for a specified list of database fields (all others are enabled).
- editfield -- begins editing of the specified field.
- editfieldname -- opens the data sheet window's field properties inspector and selects the field name.
- Field Blueprint Dialog -- examining and modifying the raw specification of a field.
- Field Properties -- available field attributes.
- Field Properties Panel -- examining and modifying field attributes.
- Field Width -- adjusting the width of a field in the data sheet.
- fieldalignment( -- returns the alignment of a database field.
- fieldformula( -- returns the formula associated with a database field.
- fieldname -- changes the name of the current field.
- fieldnumber( -- returns the number of a database field (starting with 1).
- fieldpattern( -- returns the output pattern associated with a database field.
- fieldtype -- changes the data type of the current field.
- fieldtypes -- returns a carriage return delimited array with list of fields and field data types.
- fieldtypes( -- returns a carriage return delimited array with a list of the fields and field data types.
- fieldwidth( -- returns the width (in the data sheet) of a database field.
- findreplacedialog -- opens the Find & Replace dialog.
- firstcolumn -- moves to the first column in the data sheet (leftmost column).
- getfieldproperties( -- returns a dictionary containing all of the properties of the specified field. (See the setfieldproperties statement if you want to change one or more field properties.)
- hiddenfields( -- returns a list of hidden fields in the curent data sheet window
- hidecurrentfield -- hides the current field in the data sheet.
- hidefieldsbetween -- shows all fields except those in between specified numbers.
- hidelineitemfields -- hides all line item fields.
- hidethesefields -- hides specific fields in the data sheet, making all others visible.
- Hiding and Showing Fields -- temporarily hiding fields in the data sheet.
- info("datatype") -- returns the data type of the current field.
- info("disabledfields") -- returns a list of disabled fields in the current database (fields that cannot be edited).
- info("enabledfields") -- returns a list of enabled fields in the current database (fields that can be edited).
- insertfield -- inserts a new field into the database in front of the current field.
- lastcolumn -- move to the last column in the data sheet (rightmost column).
- Limiting the Maximum Number of Data Sheet Columns -- adjusting the maximum number of columns displayed in data sheet windows.
- Line Item Fields -- are used for repeating items within a record
- mergefieldsdialog -- opens the standard *Merge Fields* dialog.
- Merging Adjacent Fields -- merging two fields into one.
- movefieldbefore -- moves the current field to a new position.
- newdatabasewithfields -- creates a new database with one or more fields.
- newdatabasewithtemplate -- creates a new database with a template.
- Numeric Data -- numeric data (fixed and floating point).
- Numeric Patterns -- control how a number is displayed or converted to text.
- Rearranging Field Order -- rearranging the order of fields in the data sheet.
- reorderfieldsdialog -- opens the Reorder Fields dialog.
- serverdatabaseconsoledump -- dumps the raw contents of the specified database on the server to the console in comma delimited format.
- setfieldnames -- changes the names of all database fields at once.
- setfieldproperties -- modifies one or more properties (name, data type, formula, etc.) of the current field.
- showallfields -- makes every field in the data sheet visible.
- showcolumns -- forces Panorama to display specified fields.
- showfields -- forces Panorama to display specified fields.
- showfieldsbetween -- hides all fields except those in between specified numbers.
- showhidefieldsdialog -- opens the standard Show/Hide Fields dialog (in the Fields menu).
- showthesefields -- makes specific fields in the data sheet visible, hiding all others.
- Smart Dates -- keyboard entry of dates.
- splitfielddialog -- opens the standard *Split Field* dialog.
- Splitting a Field -- splitting a field into two fields.
- tokenname( -- returns the name of a field or variable (instead of the value contained in the field or variables).
- visiblefieldnumbers( -- returns a data array of visible fields (by number) in the data sheet.
- visiblefields( -- returns a list of visible fields in the data sheet.
History
| Version | Status | Notes |
| 10.0 | No Change | Carried over from Panorama 6.0 |