The Select Duplicates command (in the Search menu) provides a fast and easy way to locate duplicate information in a database. The Select Duplicates command does not remove the duplicates, it simply selects them so you can examine them. You can then decide what to do about each duplicate on a case-by-case basis. You may select duplicates based on a single field (for example, all duplicate company names), on multiple fields (for example, all records with duplicate address, city, and state), or on a formula that may combine fields or use partial fields (for example, all records containing duplicate area codes).
To select duplicates based on a single field, start by using the Sort Up command to sort the database by that field. If the database is not sorted, the Select Duplicates command will warn you. For example, here is a conference registration database that may contain duplicate company information. It has been sorted into alphabetically order by company.
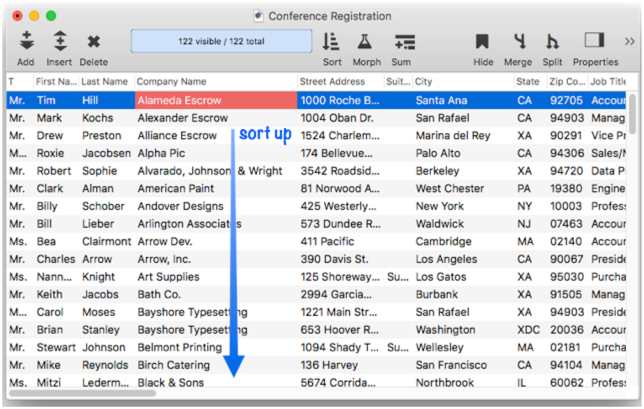
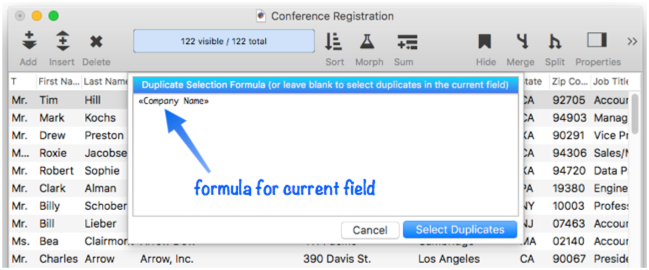
After the database is sorted, choose the Select Duplicates command from the Search menu. (Make sure you have clicked on the field you want to check for duplicates before selecting the command.) This command opens a dialog box with the formula for the current field pre-entered.
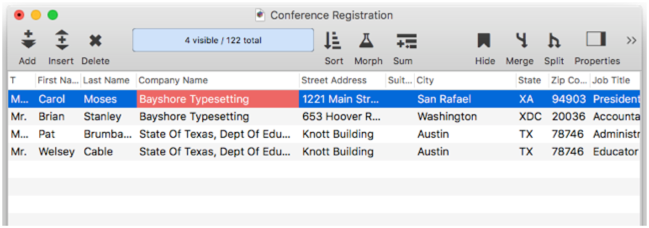
When you press the Select Duplicates button, Panorama will select the records that contain duplicate information (if any), making everything else invisible. As you can see, there are two possible sets of duplicate companies in this database.
Select Duplicates Using a Formula
To select duplicates based on multiple and/or partial fields, you’ll need to use a formula. The formula tells Panorama exactly what data should be checked for duplicates. For example, the Conference Registration database used in the previous example contains separate fields for first and last names. This formula could be used to check for duplicate names:
«First Name»+«Last Name»
If you wanted to check for duplicates using the first initial and the last name, you would use this formula (see Text Funnels to learn how [1,1] extracts the first character):
«First Name»[1,1]+«Last Name»
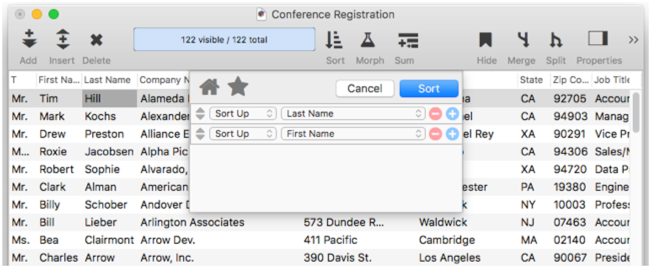
This formula would tell Panorama to treat John Doe, Joan Doe, and Jeff Doe as duplicates because they all have the same first initial and last name. Let’s search for duplicates in our conference registration file. Start by using the Sort Dialog to sort up by Last Name and First Name (see Sorting Data to learn about this dialog.
Now open the Select Duplicates command, and type in the formula that combines the first initial and last name:
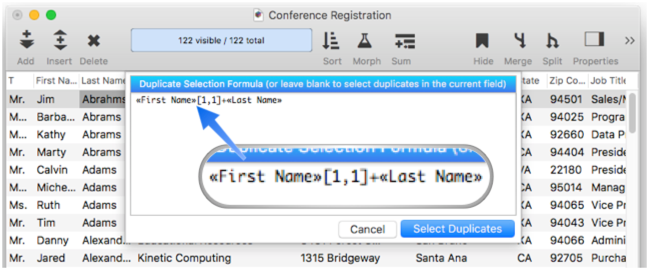
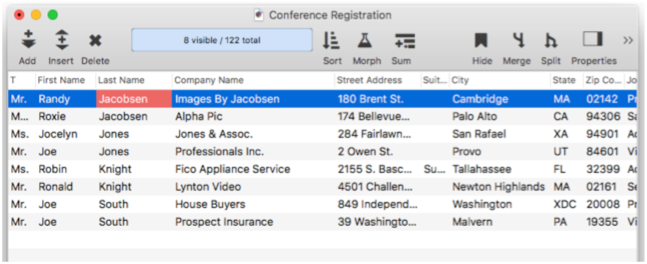
Here is the final result. There are two R Jacobsen’s (Randy and Roxie), two J Jones (Jocelyn and Joe), two R Knights (Robin and Ronald), and two J South’s (both Joe).
Note: The formula must produce a text result. Date fields must be converted to text with the datepattern( function.
See Also
- checkemptyselection -- notifies the user if a selection failed, and reverts to the previous selection.
- Date Search Options -- searching dates within a database.
- Duplicate Removal with Unpropagate -- using the unpropate command to remove duplicate data.
- Favorite Searches -- saving and recalling favorite searches.
- find -- locates the first visible record in the active database for which the specified condition is true.
- Find & Replace Dialog -- finding and replacing a word or phrase (with an option to use a regular expression).
- Find/Select Dialog -- using a dialog to search for specific data.
- findabove -- locates the next previous record (above the current record) in the active database for which the specified condition is true.
- findbackwards -- locates the last visible record in the active database for which the specified condition is true.
- findbelow -- locates the next visible record (below the current record) in the active database for which the specified condition is true.
- findid -- locates a record in the active database by its ID number (see info("serverrecordid").
- findnth -- finds the nth (2nd, 3rd, 4th, etc.) record that matches a true-false test.
- findselect -- opens the standard *Find/Select* dialog.
- findselectdialog -- opens the standard *Find/Select* dialog.
- Formula Search -- searching with a formula.
- Handling Empty Selections in Code -- dealing with an empty selection data set.
- ifselect -- combines the select and if info("empty") operations into a single statement.
- info("empty") -- returns true or false depending on the result of the last select operation. If no records were selected the function will return true, otherwise it will return false.
- info("found") -- returns true or false depending on whether the last *find* or *next* statement was successful.
- info("selectduplicatesortwarning") -- works with the selectduplicatesnowarning statement to ascertain whether or not the database was sorted correctly when last search for duplicates was performed.
- nextmatch -- locates the next visible record in the active database for which the condition specified in the most recent Find statement is true.
- Numeric Search Options -- searching numbers within a database.
- pleaseselectall -- makes sure that all records are selected.
- previousmatch -- locates the previous (closer to the top) visible record in the active database for which the condition specified in the most recent Find statement is true.
- Record Search Options -- searching via record attributes.
- Refining a Selection -- selecting a subset or superset of a previous selection."
- removeselected -- deletes all selected records from the database.
- removeunselected -- deletes all unselected records from the database.
- safeselect -- makes visible only those records for the active database for which the specified condition is true. If no records match, the previous selection is retained.
- safeselectwithin -- makes visible only those previously selected records in the active database for which the specified condition is true. If no records match, the previous selection is retained.
- search( -- searches through an item of text looking for a character, word or phrase. If it finds an exact match (including upper/lower case) with the character, word or phrase, it returns its position within the text item. If it does not find the character, word or phrase, it returns zero.
- searchanycase( -- searches through an item of text looking for a character, word or phrase. If it finds a match (upper/lower case may be different) with the character, word or phrase, it returns its position within the text item. If it does not find the character, word or phrase, it returns zero.
- Searching -- searching a database to find or select information.
- select -- makes visible only those records for the active database for which the specified condition is true.
- selectadditional -- adds unselected records to a previously selected group if they match the true-false test.
- selectall -- makes every record in the database visible.
- selectduplicates -- selects records containing duplicate information in the database.
- selectduplicatesnowarning -- selects records containing duplicate information in the database.
- Selecting with the Context Menu -- searching for information related to the current cell.
- selectreverse -- makes every visible record invisible, and every invisible record visible.
- selectwithin -- uses a Boolean formula to exclude records from a previously selected group.
- Text Search Options -- searching text within a database.
History
| Version | Status | Notes |
| 10.1.1 | New | New in this version, but similar to a feature in Panorama 6. |